Use the Linear Interpolation dialog to interpolate data from one or more ordered or finite element zones onto a destination zone. Irregular I-ordered data cannot be used for the source zones in linear interpolation; you may be able to first create a finite element zone from an irregular, I-ordered zone by using triangulation. (See Section 20 - 10 “Irregular Data Point Triangulation”.)
Linear interpolation finds the values in the destination zone based on their location within the cells of the source zones. The value is linearly interpolated to the destination data points using only the data points at the vertices of the cell (or element) in the source zone(s).
To perform linear interpolation:
1.Read the dataset to be interpolated into Tecplot 360 EX (the source data).
2.Read in or create the zone onto which the data is to be interpolated (the destination zone).
3.From the Data menu, choose Interpolate>Linear.
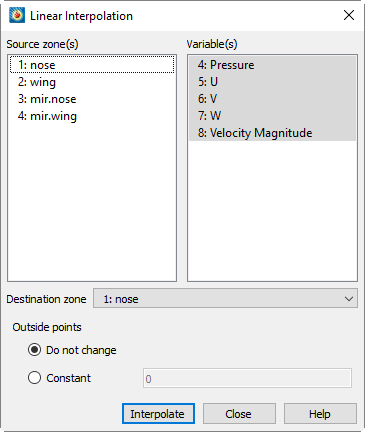
4.From the Linear Interpolation dialog, select the zones to be interpolated from those listed in the Source Zone(s) scrolled list.
5.Select which variables are to be interpolated from those listed in the Variable(s) scrolled list.
6.Select the destination zone into which to interpolate. Existing values in the destination zone will be overwritten.
7.Outside Points - Optionally, choose how to treat points that lie outside the source-zone data field. You have two options:
• Do Not Change - Preserves the values of points outside the data field. Do Not Change is appropriate in cases where you are using one interpolation algorithm inside the data field, and another outside.
• Constant - Sets all points outside the data field to a constant value that you specify.
8.Click the [Interpolate] button to perform the interpolation.
9.While the interpolation is proceeding, a working dialog appears showing the progress of the interpolation
|
|
.
 If you select [Cancel] during the interpolation process, the interpolation is terminated prematurely. The destination zone will be left in an indeterminate state, and you should redo the interpolation.
If you select [Cancel] during the interpolation process, the interpolation is terminated prematurely. The destination zone will be left in an indeterminate state, and you should redo the interpolation.