21 - 3 Identifying Field Variables
Data analysis is performed on data in the active frame. Many of these calculations require information about what the data represents. For example, if you wish to calculate pressure from your data you must identify two other thermodynamic state variables with which Tecplot 360 EX can perform the calculation using the thermal equation of the state. X, Y, and Z are taken from the axis assignments for the 2D or 3D plot in the active frame. The FLUENT and PLOT3D data loaders supply most or all of the remaining information to Tecplot 360 EX. You may also supply this information using the Field Variables dialog.
For a layout with multiple datasets, separate settings are maintained for each dataset. You can copy the settings from one dataset to another using the Save Settings and Load Settings options in the Analyze menu. These actions also transfer the settings made in the Fluid Properties, Geometry and Boundaries, Reference Values, and Unsteady Flow Options dialogs.
You must have data in the active frame to open the Field Variables dialog. The Field Variables dialog is shown below
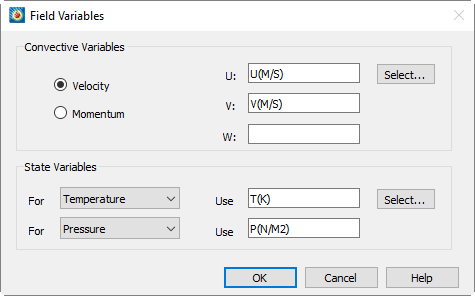
The top section of the dialog allows you to specify a vector of convective variables, either velocity or momentum (velocity multiplied by density). The bottom section of the dialog contains two drop-down menus and associated text fields for identifying two thermodynamic state variables in your dataset.
|
|
21 - 3.1 Choosing the Convective Variables
Select the convective variables in your dataset by clicking the [Select] button in the top section of the Field Variables dialog. Choose one of the two options on the Field Variables dialog to indicate whether these variables represent pure velocity or momentum.
|
|
21 - 3.2 Identifying State Variables
The State Variables region of the dialog allows you to identify up to two variables, such as pressure and temperature, in your data. From the two drop-downs, select any two choices from the types: Pressure, Temperature, Density, Stagnation Energy, Mach Number, or Not Used. Then click Select, and choose the corresponding variable(s) from your data. If you have only one thermodynamic variable, select "Not Used" in one of the drop-downs. For incompressible flow, (see Section 21 - 1.1 “Specifying Incompressible Fluid Properties”) you may specify Pressure for one variable, and you may specify Temperature or Stagnation Energy (per unit volume) for the other.
|
|
The [Select] button launches the Select Variables dialog which allows you to select variables in your dataset. The selections in the drop-down menus mentioned above determine whether these variables represent pressure, temperature, density, stagnation energy or Mach number.
 The variables selected in the Field Variables dialog are per unit volume.
The variables selected in the Field Variables dialog are per unit volume.  The convective variables used in data analysis are
The convective variables used in data analysis are  Temperature must be in absolute units, such as Kelvin or Rankin.
Temperature must be in absolute units, such as Kelvin or Rankin.